- +44(0)1332 291972
- convertme@convert-av.com
Large, heavy-industrial organisations (e.g. Military and Aerospace, Rail, Oil & Gas) operate large-footprint, complex, indoor/outdoor sites with many thousands of mobile, high-value, high-integrity assets (people, tools, equipment, materials) that need to be managed and located over their lifetime to; maintain budgetary control, reduce theft/loss, remain safety-compliant, and increase operational efficiency.
Intelligent tags support greater process integration into business operations, offering greater value-add, especially in strict compliance, safety-critical environments. No more lost, damaged or uncalibrated equipment.
iTag messaging also provides a direct 2-way message interface to the tag/operative via application-driven process-rules (e.g., return this tool for calibration) or autonomously via environmental/location-based parameters (e.g. this device is not allowed outside these boundaries), further adding value especially in safety critical environments.
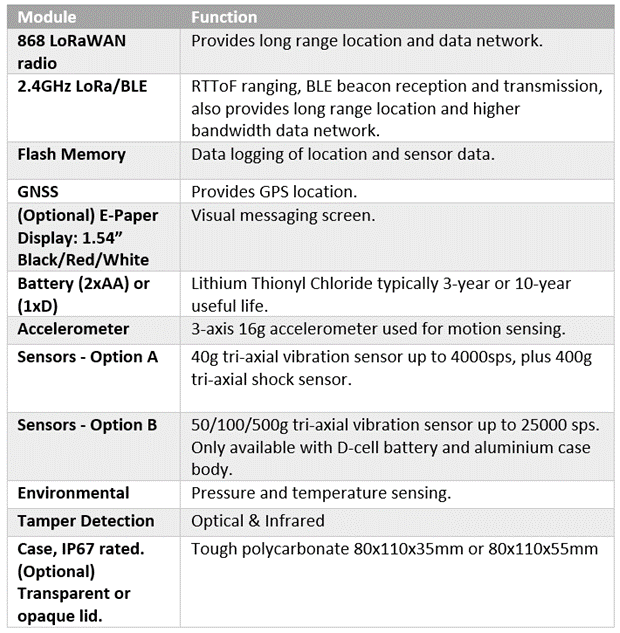
i-Tag (Standard)
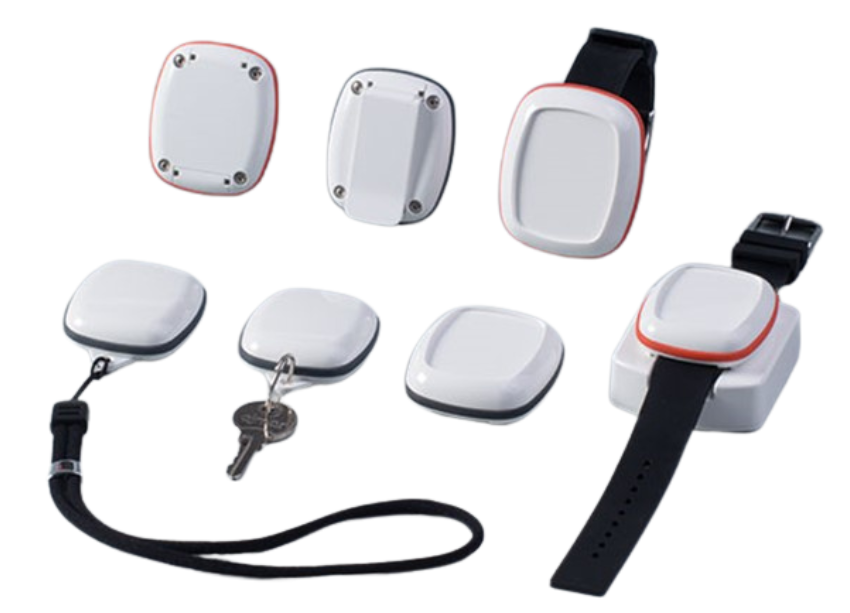

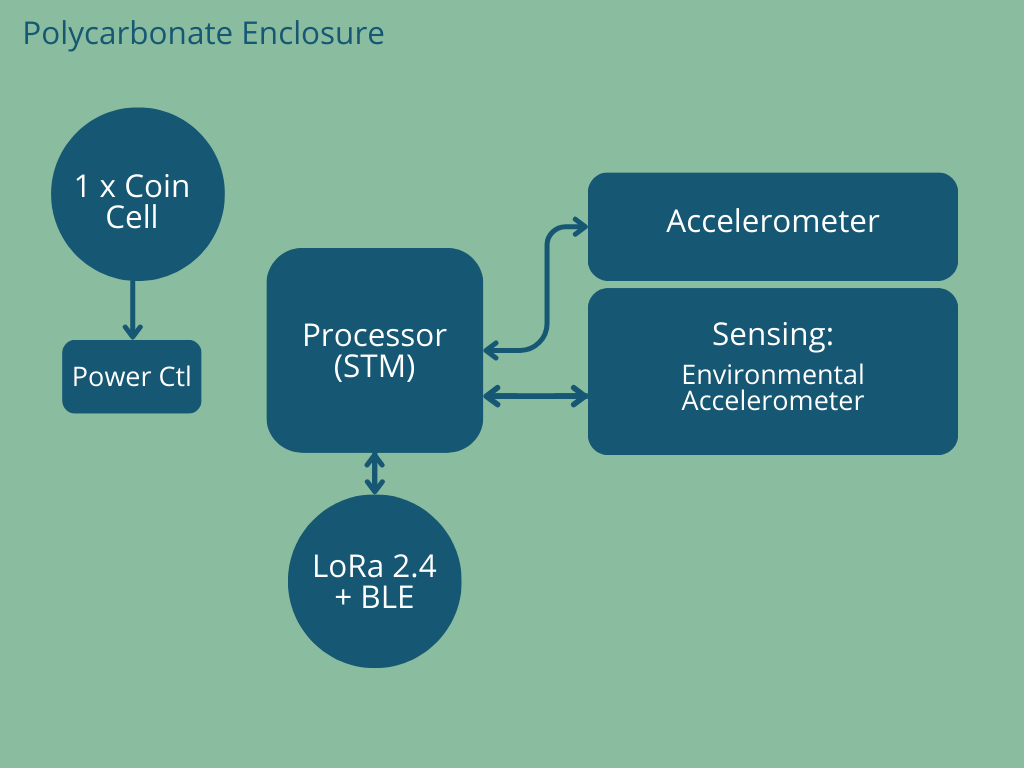
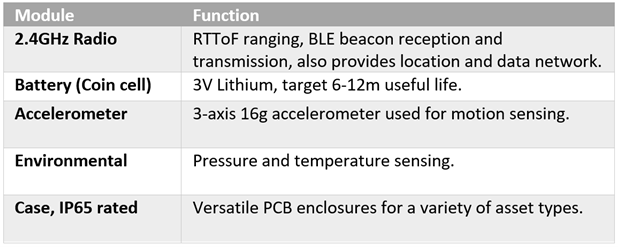
i-Tag (EPD)


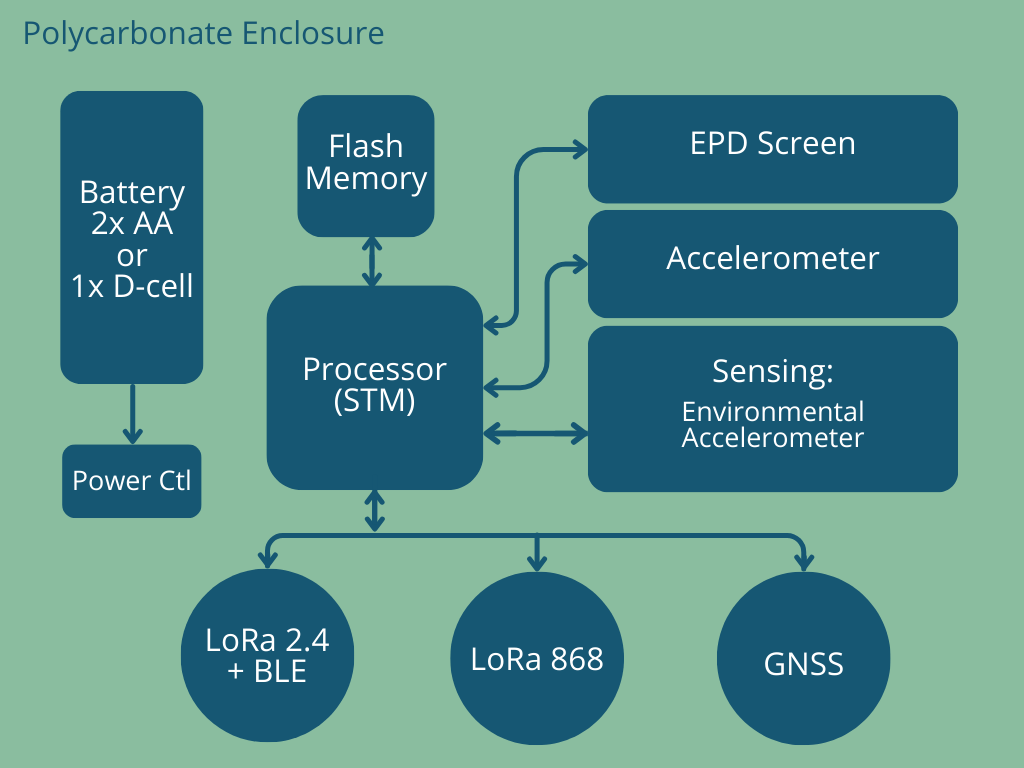
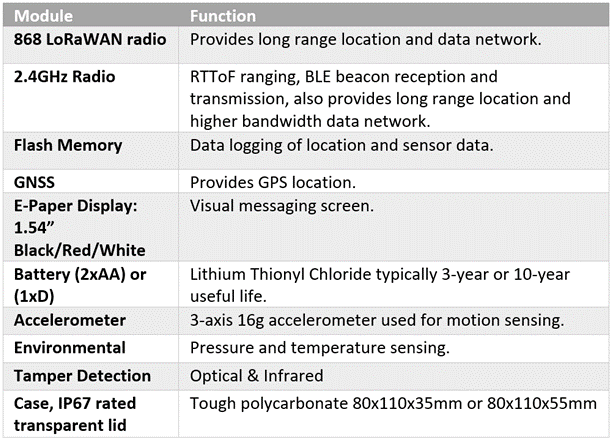
Flex i-Tag

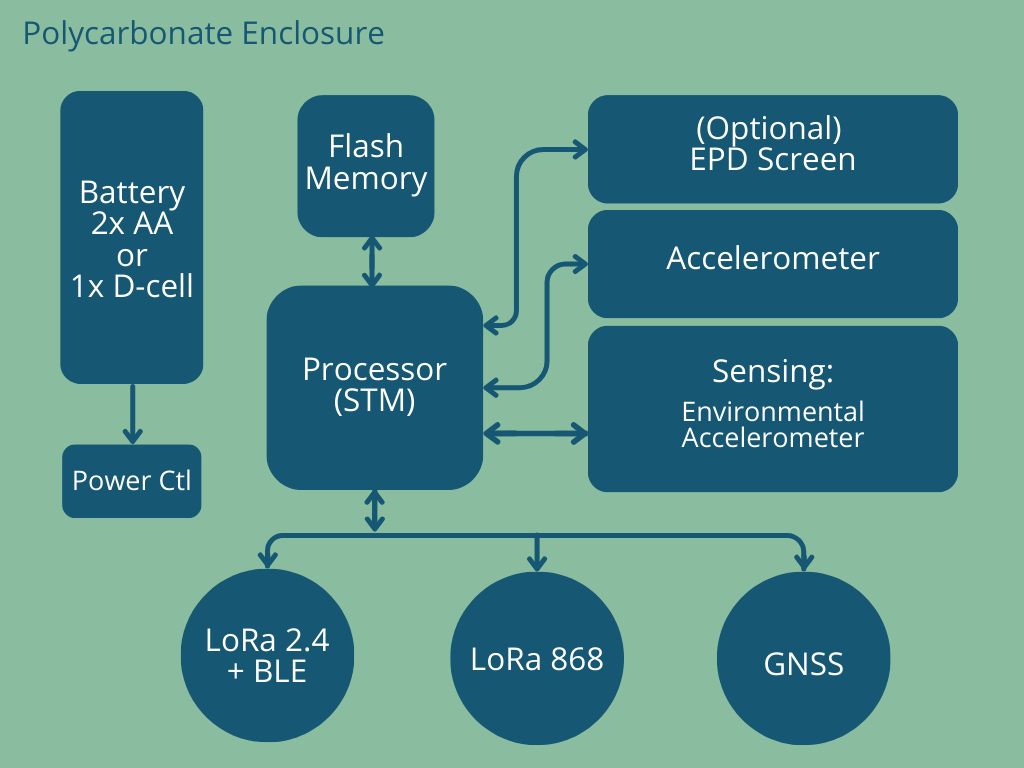
An early design decision was taken to separate the sensor electronics from the radio electronics as shown in the Flex i-Tag PCB Stack-up image below. The sensors are mounted on a small PCB which is hard mounted onto the casework, a second PCB carries batteries; and the CPU, radios and location electronics are mounted on a third PCB.
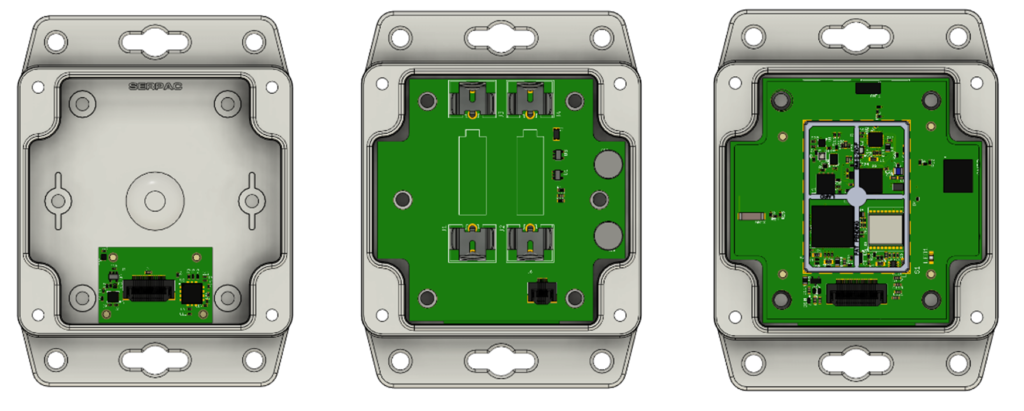
This approach allows multiple sensor solutions to be developed without altering the radio PCB (which is subject to compliance controls). Using the separate sensor board supports further (and parallel) development of more sophisticated sensors without disturbing the sensitive radio electronics, as well as offering more effective mounting options for sensor related electronics.
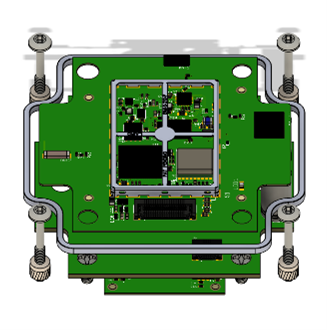
Flex i-Tag PCB Stack-up
Location services are possible via four different approaches:
A flexible approach to location management allows effective balancing of accuracy, infrastructure, and cost, which may change in different environments or applications. For instance, reporting location through a manufacturing facility will have very different requirements compared to reporting the location of a largely static asset in a secure bunker .
Feedback from our clients has largely been centred around understanding one of their key system criteria; the importance of power requirements, as part of the design considerations of the Intelligent Tags. During the requirements phase, Convert include a power budget spreadsheet which details power requirements of onboard sensors, data transport networks, and location features, to provide accurate guidance against battery choice, size and expected operating life.
The current design provides tag power via two replaceable AA cells. However, Convert have experience using rechargeable solutions, also incorporating inductive charging if required.
The entire Location/IoT ecosystem is protected via strong security protocols originally developed to support the LoRaWAN standard operating at sub-Gig frequencies. Devices connect to the network via authenticated Over-The-Air Activation (OTAA), and communicate via secure, encrypted channels. All encryption is generated via 128-bit AES key exchange. See link below for further details…
Top uses cases where intelligent asset tags (i-Tags) benefit organisations in the Rail, Military & Aerospace, and Healthcare Logistics sectors will include:
ON SITE TRACK AND TRACE / PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE / REMOTE MONITORING & CONTROL / DATA COMMUNICATION

